Diagnostic Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy

Laparoscopy, also known as minimally invasive surgery or keyhole surgery, is a surgical technique used to examine and treat conditions within the abdomen and pelvis. It involves making small incisions through which a laparoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera) and specialized surgical instruments are inserted. This approach allows surgeons to perform procedures with less pain, quicker recovery times, and minimal scarring compared to traditional open surgery.laparoscopy often reduces the risk of postoperative complications such as infections and hernias, and decreases hospital stay durations, which contributes to lower overall healthcare costs. Its use spans various fields including gynecology, urology, and gastroenterology, demonstrating its versatility and effectiveness in modern surgical practice.
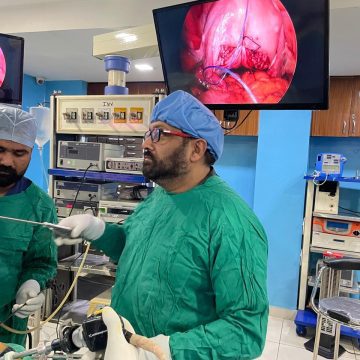
Operative Laparoscopy & Hysteroscopy
Data Research
Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident.
Data Product
Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident.
Data Security
Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident.
Successful Projects
Curabitur in eleifend turpis, id vehicula odio soluta nobis.
Creative Approach
Curabitur in eleifend turpis, id vehicula odio soluta nobis.
How Laparoscopy Works
Procedure Steps:
Anesthesia
The patient is given general anesthesia to ensure they are unconscious and pain-free during the procedure.
Incisions
Small incisions (usually 0.5 to 1.5 cm) are made in the abdominal wall.
Insufflation
Carbon dioxide gas is introduced into the abdomen to inflate it. This creates a working space and allows better visualization of the organs.
Insertion of Laparoscope
A laparoscope is inserted through one of the incisions. The camera transmits images to a monitor, providing a clear view of the internal organs.
Insertion of Surgical Instruments
Additional small incisions are made to insert specialized surgical instruments.
Surgery
The surgeon performs the necessary procedure using the instruments, guided by the images on the monitor.
Completion
After the procedure, the instruments are removed, the gas is released, and the incisions are closed with sutures or surgical tape.
Applications of Laparoscopy
Diagnostic Laparoscopy:
Pelvic Pain:
To identify the cause of chronic pelvic pain.
Infertility:
To diagnose conditions affecting fertility, such as endometriosis or pelvic adhesions.
Unexplained Symptoms:
To investigate unexplained abdominal or pelvic symptoms.
Therapeutic Laparoscopy:
Appendectomy
Removal of the appendix.
Cholecystectomy
Removal of the gallbladder.
Hysterectomy
Removal of the uterus.
Ovarian Cyst Removal:
Removal of cysts from the ovaries.
Endometriosis Treatment:
Excision or ablation of endometriotic tissue.
Hernia Repair:
Repair of abdominal hernias.
Bariatric Surgery:
Weight loss surgeries, such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy.
Cancer Treatment:
Removal of tumors or lymph nodes.
Benefits of Laparoscopy
Minimally Invasive:
Smaller incisions lead to reduced scarring.
Less postoperative pain.
Lower risk of infection.
Quicker Recovery:
Shorter hospital stays.
Faster return to normal activities.
Improved Precision:
Enhanced visualization of the surgical area.
Better outcomes for complex procedures.
Reduced Complications:
Lower risk of complications such as adhesions and wound infections.
Risks and Limitations
Risks
Infection
Though less common than in open surgery, there is still a risk of infection.
Bleeding
Potential for internal bleeding, although rare.
Organ Injury:
Accidental injury to surrounding organs or structures.
Complications from Anesthesia:
As with any surgery requiring general anesthesia, there are risks associated with anesthesia.
Limitations
Complex Procedures
Not all surgical procedures can be performed laparoscopically, especially if the condition is too complex or widespread.
Surgeon Expertise
Requires specialized training and experience. The outcomes depend significantly on the surgeon's skill.
Conversion to Open Surgery:
In some cases, the procedure may need to be converted to open surgery if complications arise or if better access is needed.
Preparation and Recovery
Preparation:
Medical Evaluation
Preoperative assessment including medical history, physical examination, and necessary blood tests or imaging studies.
Fasting
Patients are usually instructed to fast for several hours before surgery.
Medication
Instructions on which medications to take or avoid before surgery.
Recovery:
Postoperative Care
Monitoring in the recovery room until the effects of anesthesia wear off.
Pain Management
Pain relief medication as needed.
Wound Care
Instructions on how to care for the small incisions.
Activity Restrictions
Gradual return to normal activities, avoiding heavy lifting or strenuous exercise initially.
Follow-Up
Postoperative follow-up appointments to monitor recovery and address any concerns.
